Following the accelerated pace of depreciation and worsening inflation expectations since the middle of March, there was an unexpected decrease in Turkey's April inflation figure.
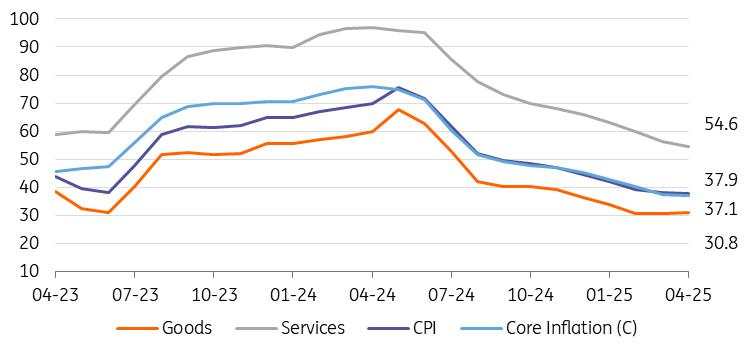
Turkey's inflation reading was 3.0% month-on-month in April, coming in below the consensus of 3.1% (and our call at 3.2%) thanks to relatively benign unprocessed food prices. As a result, the annual inflation rate, which has been declining over the past year, fell slightly to 37.9% from 38.1% in March. However, it remains above the Central Bank of Turkey's (CBT) forecast of 24% (with a forecast range of 19-29%). While inflation rose by 3.2% in April 2024, the five-year average for April in the 2003-based index was 3.1%, indicating no meaningful base effect this year.
PPI was 2.8% MoM driven mainly by food products, textiles and metals, while there was a drop in the annual change to 22.5% YoY vs a month ago. The 6.5% MoM and 3.9% MoM increases in the currency basket (50:50 EUR:USD) in March and April, respectively, showed an acceleration compared to previous months and signalled that the pass-through from exchange rates to prices has been more pronounced lately. However, the year-on-year lira increase remained relatively muted at less than 23%, implying that cost pressures have been contained. This has contributed to a more favourable trend in Turkish lira (TL)-denominated import prices along with benign commodity prices, given the large drop in April.
Core inflation (CPI-C) rose by 3.3% MoM, bringing the annual rate down to 37.1%. A preliminary assessment of seasonally adjusted data – set to be published by TurkStat and closely monitored by the CBT to gauge underlying trends – reveals that the acceleration in March headline and core numbers also continued in April, while the pace of increase in core was more evident.
Inflation outlook (%)
Source: TurkStat, ING
Breaking down the data, we can see that:
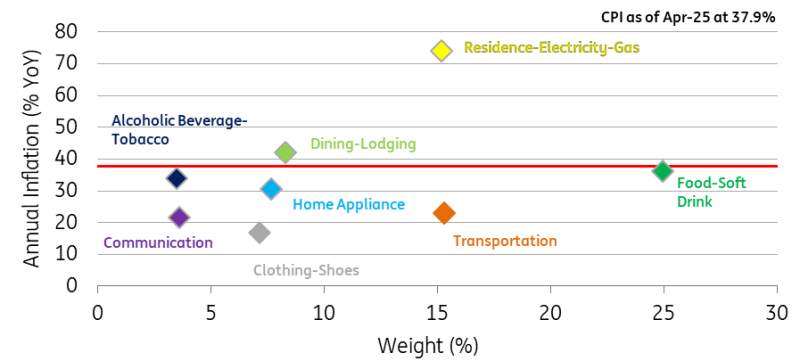
Housing was the biggest contributor at 0.74 percentage points (ppt), driven by a 25% hike in household electricity prices.
This was followed by transportation at 0.57ppt, on the back of automobile price adjustments following the currency weakness and higher prices in transportation services. The decline in oil prices, on the other hand, limited the inflationary pressures in this group.
The food sector was once again another big contributor to the headline figure, adding 0.51ppt. Monthly inflation in this sector, however, remained below the level in the same month of 2024 thanks to the price drop in fresh fruits and vegetables. The benign food inflation contributed to a lower-than-expected April reading.
Finally, clothing pulled the headline up by 0.37ppt. However, annual inflation in this group has remained low at 16.9%.
Consequently, goods inflation inched up to 30.8% YoY, while core goods inflation – considered a better indicator of the trend – stood at 20.3% YoY.
Services inflation, which is less affected by currency fluctuations but more influenced by domestic demand and minimum wage increases, continued to decline. It dropped to 54.6% YoY, marking the lowest level since summer 2022 thanks to further easing in rents.
Annual inflation in expenditure groups
Source: TurkStat, ING
Read the original analysis: Softer-than-expected Turkish inflation in April despite recent lira weakness
作者:ING Global Economics Team,文章来源FXStreet,版权归原作者所有,如有侵权请联系本人删除。
风险提示:以上内容仅代表作者或嘉宾的观点,不代表 FOLLOWME 的任何观点及立场,且不代表 FOLLOWME 同意其说法或描述,也不构成任何投资建议。对于访问者根据 FOLLOWME 社区提供的信息所做出的一切行为,除非另有明确的书面承诺文件,否则本社区不承担任何形式的责任。
FOLLOWME 交易社区网址: www.followme.asia


加载失败()