On August 1, the United States published an updated list of its “reciprocal” tariffs. While this new version provides some clarity, it does not offer a long-lasting explanation of the Trump administration's protectionist policy. In the short term, it changes the game for certain countries, particularly India and China.
The apparent logic of the new tariff schedule
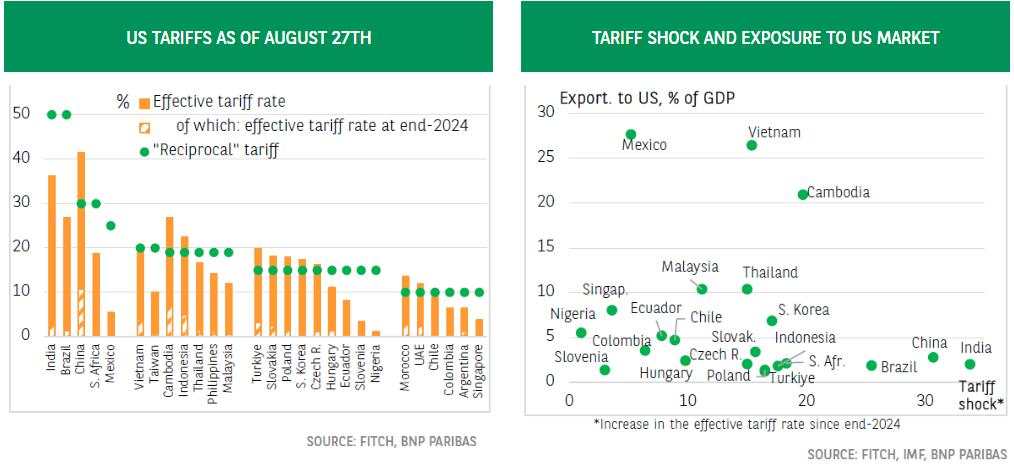
For countries having a trade deficit with the United States, the 10% floor rate introduced on April 2 remains in place. Therefore, there is no change for most countries in Latin America, Africa, and the Middle East, or for Singapore. Brazil is a major exception with a 50% tariff – a punitive tax motivated by political reasons.
For countries having a trade surplus with the United States, reciprocal tariffs now range from 15% to 50%. A 15% tax is applied to countries that either have reached a compromise with the United States (such as the European Union and South Korea) or have a limited bilateral trade surplus and/or have at least begun discussions with Washington. These include various countries such as Turkey, Ecuador, Nigeria, and African textile-exporting countries such as Madagascar.
Asian countries posting large trade surpluses with the US were among those most affected by the announcements on “Liberation Day” on April 2. Most have begun negotiations, and agreements with Vietnam, Indonesia, and the Philippines have been announced. The new reciprocal tariffs remain high, set at 19% or 20% for Taiwan (vs. 32% announced in April) and ASEAN countries (vs. 46% initially planned for Vietnam and 36% for Thailand) – with the exception of Myanmar and Laos (40%).
A few special cases. For India, the new tariff is 25%, but a 25% penalty has been added since August 27, pending a possible agreement with Washington. This surcharge is officially intended to punish India for its purchases of Russian oil. South Africa has also failed to reach an agreement, and its 30% tariff is maintained. Finally, for China (current tariff of 30%) and Mexico (25%, applied to goods traded outside the USCMA), the truce will last another 90 days, allowing negotiations to continue.
All uncertainties regarding the evolution of tariffs are far from being resolved. First, discussions between Washington and Beijing, as well as negotiations to finalize all bilateral trade agreements, are ongoing. Reversals by the Trump administration are also possible for political or legal reasons (for instance if the US Supreme Court invalidates the tariffs justified by the IEEPA). Secondly, the implementation of tariffs on goods originating in China but transiting through third countries (a 40% surcharge is planned) remains highly uncertain and complex (how can “transshipped” goods be identified?). Finally, Washington continues to modify sectoral taxes. The average effective tariff rates applied to each country are therefore likely to continue to evolve.
Read the full article
Được in lại từ FXStreet, bản quyền được giữ lại bởi tác giả gốc.
Tuyên bố miễn trừ trách nhiệm: Quan điểm được trình bày hoàn toàn là của tác giả và không đại diện cho quan điểm chính thức của Followme. Followme không chịu trách nhiệm về tính chính xác, đầy đủ hoặc độ tin cậy của thông tin được cung cấp và không chịu trách nhiệm cho bất kỳ hành động nào được thực hiện dựa trên nội dung, trừ khi được nêu rõ bằng văn bản.


Tải thất bại ()